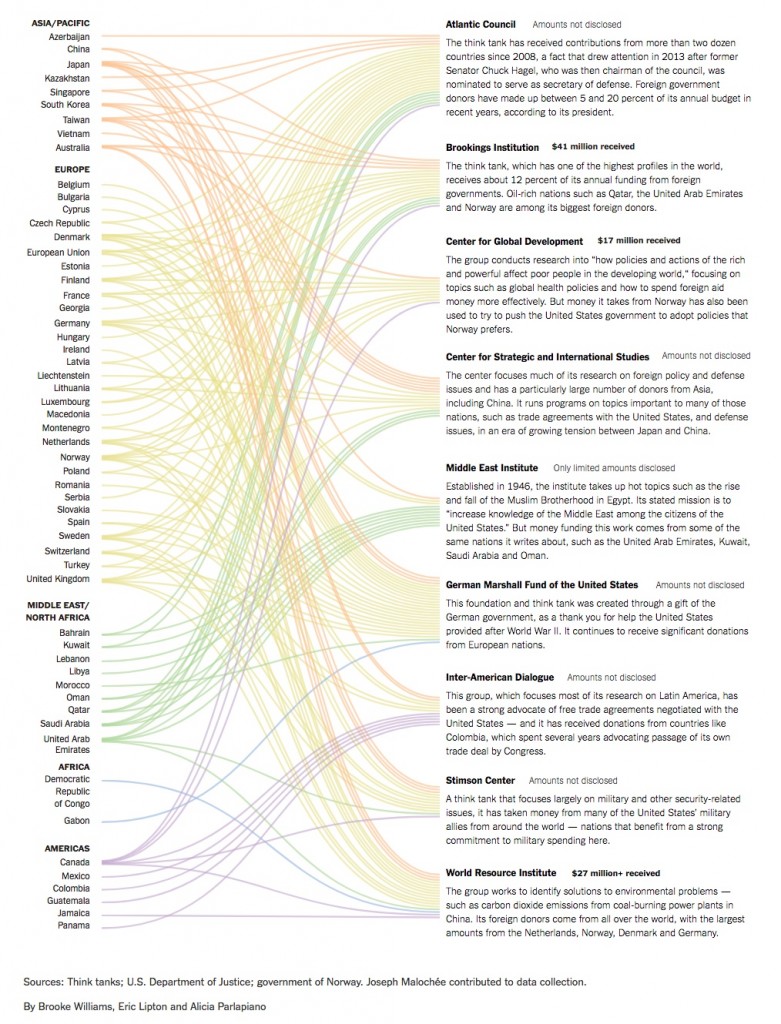
Founded in 1961, the Atlantic Council (AC) is part of the NATO offshoot Atlantic Treaty Association, described as an umbrella organization which acts as a network facilitator in the Euro-Atlantic and beyond, that claims to draw together “political leaders, academics, military officials, journalists and diplomats in an effort to further the values set forth in the North Atlantic Treaty, namely: democracy, freedom, liberty, peace, security, and the rule of law”.
Atlantic Council’s board members include Henry Kissinger, former CIA chiefs Michael Hayden and Mike Morell, Bush-era head of Homeland Security, Michael Chertoff, and Richard Edelman, head of the world’s biggest public relations company, which has been attacked for its relationship with climate change denial campaigns. Its Digital Forensic Research Lab is led by a former Obama National Security Council advisor, and it is partnering with Facebook to carry out a purge of pages it deems to be “fake news”.
Together with the Americas Society/Council of the Americas (AS/COA), the Wilson Center and other organisations (between which there is a revolving door for personnel), the Atlantic Council has been an international platform and promoter for both the controversial anti-corruption operation Lava Jato (Car Wash), which helped paralyse the Brazilian economy, and underpinned the 2016 removal of the Rousseff Government from power. (Update: Lava Jato then jailed former president Lula da Silva, opening the door for a Bolsonaro presidency).
The organisation insists it is independent from both the US Government and NATO, however it receives the majority of its funding, of an undisclosed total, from various NATO member governments.
It was recently in the news for donating a million dollars, provided by the US State Department, to an opposition group in Venezuela, the latest in an estimated USD$45+ million in US funding to pro-opposition groups since 2008.
In October 2013, one year ahead of a crucial run of regional elections and after a burst of destabilisation in Brazil, the Atlantic Council launched its new Latin America effort, named the ‘Adrienne Arsht Center’, with a stated aim to “study, educate, and strengthen the trends transforming Latin America into a strong Western partner”.
The center was founded by Peter Schechter, a consultant who also hosts Altamar, a foreign policy podcast. Until June 2017 he was the Atlantic Council’s Senior Vice President for Strategic Initiatives as well as founding director of its latest Lat Am-focussed wing.
Born in 1959 in Rome, Schechter was raised in Italy, Bolivia, and Venezuela. In 1993, he co-founded Chlopak, Leonard, Schechter and Associates, a DC-based consultancy which advises politicians, companies, non-profits, and international organizations. Their clients’ tasks included fighting “regulatory encroachment” on US banks in Latin America, to spinning Hunt Oil’s Camisea project in Peru, which was threatened by protest from indigenous groups.
The bulk of his work, however, was serving as election advisor to conservative and neoliberal candidates across Latin America, including a number of current presidents. Clients included Venezuela opposition leader Henrique Capriles, Alvaro Uribe (his fourth client in Colombia), and 1994-2002 Brazilian President Fernando Henrique Cardoso.
His expertise in the region has made him a regular talking head on Latin American politics. He is a frequent guest analyst for television shows across the region as well as on US-based Spanish language networks Univision and Telemundo, noted for their right-wing bias.
In September 2009, Schechter’s firm signed a contract with the interim Honduran government of Roberto Micheletti to provide public relations services following the June 28, 2009 coup d’état. According to Foreign Agents Registration filings with the US Department of Justice, the firm received over $292,000 to boost the post-coup regime’s image in the US. His work for the Honduran putschists attracted negative publicity for Schechter’s company and sparked indignation both in Honduras and in the US, including letters of condemnation and a protest in front of the firm’s Washington, DC office.
On Brazil, Atlantic Council personnel could be found quoted in the press and on television networks eulogising Operation Lava Jato, normalising the judicial/parliamentary Coup d’état which removed Dilma Rousseff, and also promoting the neoliberal programme of Michel Temer’s post-coup government, such as fiercely resisted cuts to workers rights and a programme of pension reform which would raise retirement age as high as 74 for millions of ordinary Brazilians, which is above life expectancy in some areas of the country.
When these commentators would talk about “anti-corruption” and “poor economy” as the reasons for her impeachment, they would never indicate any relationship between the two. Yet Rousseff’s removal stemmed in part from both the public fervour generated by the partisan anti-corruption operation, and also perversely the economic effects it had created – with some economists estimating that the resulting Lava Jato mandated shutdown of economic sectors in 2015 accounted for half a million unemployed in construction alone, and 2.5% of GDP – turning a mild recession into something Wall Street talking heads in its corporate media could portray as the “worst economic crisis in a century“.
In an April 2016 piece, titled “In Brazil, Is Impeachment the Answer?“, several AC staff denied a coup was taking place, with Schechter declaring that “Dilma has been the amateur hour in terms of politics for the last two years,”. “The greatest crime committed in Brazil,” he added, “was the crime of postponing, day after day, the (neoliberal) political reforms that the country needs to become the potent leader that it could be.”.
A September article by deputy director of Atlantic Council’s Latin America Center, Andrea Murta, was headlined “Brazil After Dilma: A Reason for Optimism“, and declared that Rousseff’s impeachment would “ultimately benefit Brazilian democracy.”
During the coup the Atlantic Council also held an event called “Oil & Gas in Brazil: A New Silver Lining?” lauding the imminent cut-price sell of of Brazil’s fossil fuel resources by the illegitimate Temer government.
Operation Lava Jato not only had profound effects on Brazil’s economy and democracy, it has also indirectly enabled capture of the country’s strategic resources, and corporations such as Embraer, which is now a target of takeover by US competitor, Boeing, sparking outcry amongst Brazilian developmentalists, nationalists, and the left as a whole.
It was at the Atlantic Council in June 2017 where then acting assistant Attorney General Kenneth Blanco publicly admitted that the United States Department of Justice had been collaborating informally with the Operation Lava Jato task-force – in breach of Brazilian law.
Blanco highlighted the criminal charges against former President Lula as putting Brazil at the “forefront” of countries fighting corruption. He continues saying, “At the core of the tremendous cooperation between our two countries is a strong relationship built on trust. This trust allows prosecutors and agents to have direct communications regarding evidence. Given the close relationship between the Department and the Brazilian prosecutors, we don’t need to rely solely on formal processes such as mutual legal assistance treaties, which often take significant time and resources to draft, translate, formally transmit, and respond to.” (Update: Blanco’s admission of US involvement was then used unsuccessfully as grounds for the acquittal of charges which would ultimately keep Lula da Silva out of the 2018 election. Although openly admitted, there would be no major media acknowledgement of the US role in Lava Jato until Bolsonaro was in power over 2 years later. Far more is now known about the Lawfare operation in Brazil than was at time of publication in December 2017, read all our articles on the topic here).
The roots of the operation can be traced back as far as a 2002 Bush-era initiative, encouraged by infamous Office of Public Diplomacy propagandist, former Venezuelan ambassador, and one time head of Council of the Americas, Otto Reich, which made anti-corruption the principal tool for enabling political and economic outcomes in the region.
Mr. Reich, like Schechter was also hired to propagandise on behalf of Honduras Post-Coup Government. Following the Coup, Reich sent his thoughts to members of Congress by e-mail. “We should rejoice,” he wrote to one member of the Senate Foreign Relations Committee, “that one of the self-proclaimed 21st Century socialist allies of Chávez has been legally deposed by his own countrymen.”
Also in 2009, leaked cables reveal that Lava Jato’s main protagonist, inquisitorial prosecutor/judge Sergio Moro, was already in collaboration with the State Department and Department of Justice on an embryonic strategy which would evolve into Operation Lava Jato. Brazil, a one-time ally of Venezuela, has seen its democracy, economy and sovereignty severely impacted by the operation, which has been deemed “Lawfare” and “War by other means” by observers. The ongoing role of public relations from within or around organisations like Atlantic Council and AS/COA and their relationship with large commercial news organizations warrants maximum scrutiny, and is indicative of whom is directing the real power being wrought in the region.
Using these non-conventional weapons, the so called ‘Pink Tide’ of leftist governments across the continent has been reversed, to the delight of Washington, London and Wall Street. Corruption allegations are affecting the political scene across South America, in Chile, Argentina and Peru, and frontrunner for Brazil’s own 2018 election, former President Lula, faces an appeal on 24th January in what amounts to a kangaroo court, a trial which could shape the country’s future for a generation. (Update: the appeal was rejected in controversial circumstances, frontrunner Lula was jailed for 580 days, kept out of the 2018 election, paving the way for Jair Bolsonaro’s presidency).
The role of NATO adjunct the Atlantic Council – effectively its propaganda wing – in Latin America is logical, given that the impact is not only economic and political but military and strategic. Joining its beachhead in Colombia, which is becoming an official NATO partner, comes the establishment of new US Military presences in Argentina, Paraguay, Peru and now Brazil’s Amazon and North East. It is telling that Liliana Ayalde, US Ambassador to Brazil from September 2013, throughout the 2014 election and subsequent Coup d’état, is now serving as civilian deputy commander of US Southern Command (SOUTHCOM).
[qpp]

